Remote Procedure Call (RPC) in the context of PulseChain is a protocol that one program can use to request a service from a program located in another computer in a network without having to understand the network’s details. RPC is used in blockchain technology for various purposes, primarily for interacting with PulseChain.
There is no one-size-fits-all for RPCs on a blockchain and the same goes for PulseChain. But having multiple RPCs does mean that transaction requests are dispersed between multiple providers. This dispersion reduces dependency on any one provider and has the potential to improve your user experience on services like PulseX, Piteas, Coast and Phux. We’ve had users tell us that it’s vastly improved the success of transactions on Phiat and Phamous too.
RPC URL: https://rpc.pulsechain.com/
Chain ID: 369
Currency Symbol: PLS
Explorer: https://otter.pulsechain.com/
Alt Explorer: https://scan.pulsechain.com/
If you are a PulseChain “power user” or anyone thinking about launching a project in the PulseChain Ecosystem, it’s probably worth considering the G4mm4 RPC. Coast has changed some of our internal tools over to using this RPC and we’ve noticed fewer failed transactions with higher throughput.
RPC URL: https://rpc-pulsechain.g4mm4.io
Chain ID: 369
Currency Symbol: PLS
Explorer: https://otter.pulsechain.com/
Alt Explorer: https://scan.pulsechain.com/
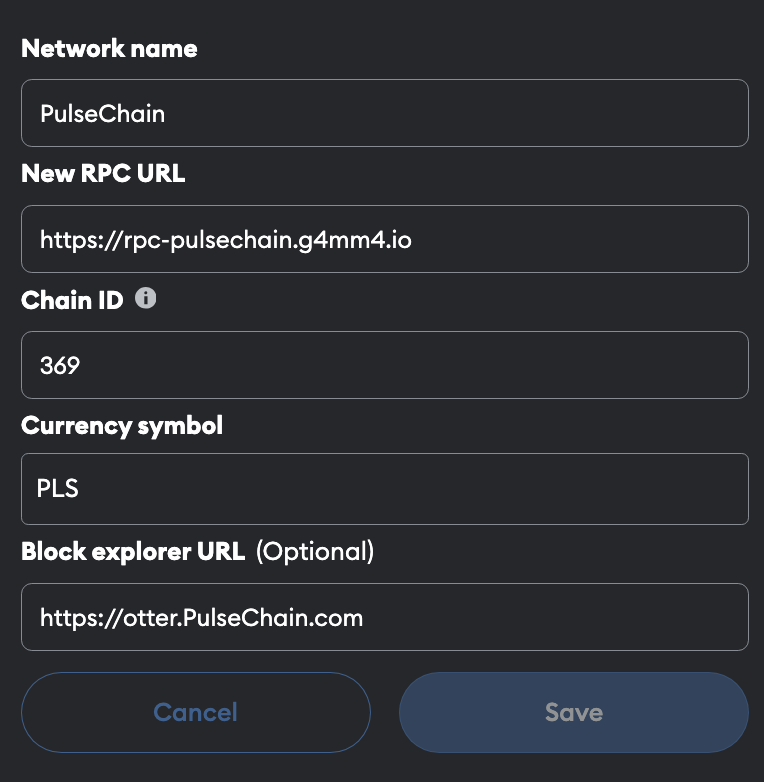
If you’re planning to change your PulseChain RPC settings in MetaMask, the screenshot below shows how the network settings should appear if you’ve changed to the G4mm4 RPC correctly:
An RPC (Remote Procedure Call) endpoint is a network communication interface that allows one program to request a service or function from another program located on a remote system. In simpler terms, it’s a way for software running on different machines to interact with each other.
Here’s how it works on PulseChain:
The term “endpoint” in this context refers to the specific location where these RPC requests are sent. It’s like the address or URL that the client program uses to communicate with the server. This endpoint contains all the necessary information for PulseChain to connect the client and server, such as IP addresses, port numbers, and sometimes the specific procedure or function.
RPC frameworks often abstract a lot of the network communication details, making it easier for developers to implement distributed systems where different parts of a program can run on different machines. Popular RPC frameworks include gRPC, XML-RPC, and JSON-RPC.
Remote Procedure Call (RPC) is a fascinating technology with several interesting aspects. Here are five notable facts about the technology as it applies to PulseChain:
Historical Significance: RPCs have been around since the 1980s. They were developed to make it easier for programmers to build software that could run on multiple computers in a network. The concept of RPCs is crucial in the evolution of distributed computing, allowing for easier communication between different systems and services.
Language and Platform Agnostic: One of the key features of modern RPC systems is that they are often designed to be language and platform agnostic. This means that a service written in one programming language (like Python) can communicate with another service in a different language (like Java), as long as both understand the same RPC protocol. This cross-language capability breaks down barriers in software development and system integration.
Use in Major Systems: RPCs are integral to many large-scale distributed systems and applications. For example, they are used in network file systems like NFS (Network File System), within operating systems for internal process communication, and in large-scale systems like Google’s internal infrastructure and various cloud computing platforms.
Variety of Protocols and Standards: There are several RPC protocols and standards, each with its unique features and use cases. Some well-known protocols include XML-RPC, which uses XML to encode calls; JSON-RPC, which uses JSON; and gRPC, developed by Google, which uses Protocol Buffers for efficient serialization. This variety allows developers to choose a protocol that best fits their application’s requirements.
Facilitation of Micro-services Architecture: RPC plays a crucial role in the micro-services architecture, a design approach where an application is structured as a collection of loosely coupled services. In such systems, RPCs are often used for service-to-service communication, enabling each micro-service to efficiently perform its specific function and communicate with other services in the system. This has revolutionized how complex applications are built and scaled in modern software development.
If you have any issues with creating a recipient or starting a transfer, please contact our support team using the website chat feature in the bottom right of the screen.
App: app.0xcoast.com
Website: 0xcoast.com
Twitter: @0xCoast
Telegram: @Coast0x